Ectropion
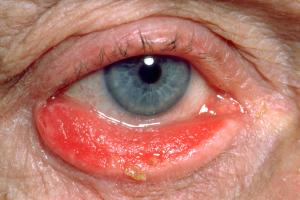
Ectropion is where the lower eyelid droops away from the eye and turns outwards. It's not usually serious, but can be uncomfortable. You should see your GP if you think you have ectropion.
Symptoms of ectropion
Ectropion mainly affects the lower eyelid and can occur in one or both eyes.
The drooping eyelid can disrupt the drainage of tears, which can make the eyes:
- sore, red and irritated
- water much more than normal
- feel very dry and gritty
- more vulnerable to bacterial infections, such as conjunctivitis
In severe cases that aren't treated, it's possible to develop a corneal ulcer (a sore on the eye's surface) that could affect your vision, but this is rare.
Ectropion is different from entropion, which is where the eyelid turns inwards, towards the eye.
When to get medical advice
Visit your optician or GP if you think you have ectropion.
They'll be able to diagnose the problem by examining your eye. They can refer you to an eye specialist called an ophthalmologist for further assessment and treatment, if necessary.
Contact your GP or GP out of hours service immediately, or go to your nearest emergency department, if your eye is very red and painful, or you have other symptoms, such as reduced vision or sensitivity to light.
This could be a sign of a more serious problem that requires urgent treatment.
Causes of ectropion
Most cases of ectropion are associated with ageing. It can occur as the tissues and muscles of the eyelids become weaker as you get older.
Less common causes of ectropion include:
- a problem with the nerves that control the eyelid – this is often seen in a type of facial paralysis called Bell's palsy
- a lump, cyst or tumour on the eyelid
- damage to the skin around the eyelid as a result of an injury, a burn, a skin condition such as contact dermatitis, or previous surgery
In rare cases, ectropion can be present from birth if the muscles under the eyelid don't develop properly.
Treating ectropion
Treatment for ectropion depends on its severity and the underlying cause. Mild cases may not need any treatment.
If it's only causing minor problems, your optician, GP or eye specialist can advise you about ways to relieve your symptoms and look after your eyes at home.
In more severe cases, an operation to fix the problem will probably be recommended.
Looking after your eyes
Your doctor may recommend using eye drops during the day and eye ointment at night to reduce irritation and keep your eye lubricated.
Try not to wipe your eyes too much, as this can pull on the eyelid and make the problem worse.
If you need to wipe your eyes, it's best to do this gently and wipe upwards and inwards (towards your nose).
If an operation is recommended, you may be advised to tape your eyelids closed at night with special skin tape, as a temporary measure to help protect your eyes while you wait to have surgery.
Surgery
Surgery for ectropion is a minor procedure and is usually carried out under local anaesthetic(external link opens in a new window / tab).
It's normally carried out on an outpatient basis, which means you won't need to stay in hospital overnight.
More useful links
The information on this page has been adapted from original content from the NHS website.
For further information see terms and conditions.